Ultimate Biology Career Guide
Your Career in Biology
A career in biology can be an immensely gratifying field of study in addition to being an exciting vocational track. The study of biology rewards those who are inquisitive, willing to make keen observations, study the evidence at hand through data-driven methodologies, and arrived at quality, scientifically-founded solutions.
As a biologist, many vocational tracks exist raging from evolution to ecological conservation to natural history. Other biologists immerse themselves in the medical fields specializing in research, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and the like. We will know turn our attention to the specifics of earning a degree in biology and details surrounding the disciplines within biology.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most frequently asked questions when it comes to a career in biology and provide a helpful overview for those who are considering this career path.
What are some Career Paths in Biology?
There are a wide range of career paths that a biologist can follow and their options are seemingly endless upon earning a college degree in biology. A few of the options include:
Health Care: Biologists who work in health care may be tasked with the creation of public health campaigns geared towards increasing public awareness and defeating a variety of illnesses such as cancer, AIDS, or tuberculosis. Other biology tracks within healthcare can include the focus to thwart a variety of rare, deadly diseases such as Ebola or Zika. If you choose a biology career in health care, expect additional education past the undergraduate level in your specific field of study. For those biologists who have a heart to assist those living in a foreign country, there are highly regarded organizations tasked to provide resources and information to those looking to improve the quality of health care in their respective country. The best known programs for professionals with a biology degree looking to advance their careers abroad include are Peace Corps and Doctors Without Borders.
Research Biology: This field focuses on the study of the natural world, through the use of state of the art tools and techniques. Research techniques can either be deployed by biologists in a laboratory or the natural environment depending on the situation. In fact, a research biologist may travel to a foreign country or a remote region of the world to gather information, collect samples, and validate data. A research biologist invests time and resources to better understand the inner workings of living organisms and/or extend our knowledge of a working theory through a variety of data-derived techniques. Their research findings are put to good use by widening our collective knowledge about a particular subject along with providing data for adjacent research projects in the offing. For more information about the breadth and depth of research projects, the American Institute of Biological Sciences has put together a list of member organizations here.
Environmental Conservation & Management: Are you passionate about solving complex environmental problems in an effort to save the planet for future generations? A biology career in the conservation and management of the environment could be a great fit for your future endeavors. Other vocational tracks within environmental conservation and management include:
Park Ranger: Park Rangers are professionals tasked to protect our natural resources and educate others about those valuable resources.
Marine Biologist: A Marine Biologist works to understand a variety of organisms that reside in the ocean or other marine bodies of water.
Wildlife Biologist & Zoologist: Both Wildlife Biologists and Zoologists study a host of wildlife and animals along with their respective ecosystem.
Biologists who work in conversation/management fields typically work alongside an array of special interest groups and landowners to create & implement sustainable management plans. Natural resource agencies, non-profit conversation companies, and wildlife rehabilitation facilities provide a vast number of employment opportunities for those who choose this particular field.
Biology Education: Biology educators work in the field, classroom, museum, and/or lab setting in an effort to teach students new biological concepts and discover novel resources for advanced educational techniques. If you select a career in biology education, you can choose a variety of work settings and employers that may include: colleges, universities, primary schools, secondary schools, aquariums, zoos, science museums, nature centers, and parks.
Other Biology Paths: In addition to the tracks listed above, there are a variety of paths you can choose to follow after earning a degree in biology. Some of these career options may include an array of the following:
Art & Journalism: Creating accurate illustrations in biology textbooks, magazines, and journals is a task that falls to those with a thorough understanding of biology. Publishing houses, magazines, and health journals can provide employment to those who choose to specialize in art or illustration within the broad-based field of biology.
Biotechnology: In the field of biotechnology, professionals apply scientific principles to create or improve upon tools and products in the marketplace. Biotechnologists can focus on genetics, nanoparticles, cell biology, molecular biology, food science, medicine, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals to name a few disciplines. A host of research topics within biotechnology can be found here.
Forensics: A forensic biologist works closely with law enforcement agencies using science to discover evidence and process it in a manner that is conducive to solve crimes. In most cases, a forensic biologist will focus on a particular specialty and work to become a subject matter expert in that field versus a generalist. Specialties within forensic biology can include: medical examiner, crime scene investigation, forensic anthropology, forensic odontology, criminalist, crime lab analyst, forensic toxicology, forensic science training, forensic psychology, forensic document examiner, forensic psychiatry, forensic pathology, forensic biotechnology, forensic entomology, and forensic computer examiner.
Math: Biologists in computational biology and bioinformatics leverage mathematics to solve a variety of biological problems ranging from gene mapping to ecosystem modeling. Mathematical biology is a relatively newer field of study that rely on computer models and deep analytics to understand and model complex research areas within biotechnology, ecosystem dynamics, and cell biology. Through the use of supercomputers and advanced modeling techniques, scientists can more efficiently process vast sums of data while vetting competing biological theories.
Business & Economics: Biologists with a business concentration may find employment opportunities with large multinational corporations such as pharmaceutical manufacturers as they are able to provide deep insights to provide helpful research and lend credibility to the public relations and marketing teams within an organization.
Politics: When new legislation is passed regarding environmental protection, political biologists are frequently consulted as part of a defined process. The inherent scientific knowledge of a political biologist can serve as the basis of new legislation and may end up being powerful political advisers behind the scenes.
How Can I Pursue a Career in Biology?
In order to successfully prepare for a fruitful career in biology, you will need to start pursuing a career in earnest while you are in high school by taking all of the required math, science, chemistry, and biology courses. It is highly recommended to talk to professional biologists in conjunction with your guidance counselors to establish a set of realistic expectations about your biology career. Invest time and resources to discover the best college program for you and learn everything you can about course requirements towards your eventual career path. Take the time to consider how long it will take to complete your degree and be sure to ask your professors about part time employment opportunities in your chosen field of biology. Lastly, summer internships are also an absolute must for a biology student to hit the ground running after graduation.
What Does the Future Hold for Biologists?
The job outlook in this field is very bright, but your ability to find employment will depend on your willingness to move as employment opportunities in certain areas of the country are more favorable than others. Job growth is expected to continue to outpace the average rate of employment growth in the U.S. with the best upward growth opportunities going to those who are flexible and willing to work hard to put themselves in the best position to capitalize on changing trends.
How Much Can I Expect to Make in Biology?
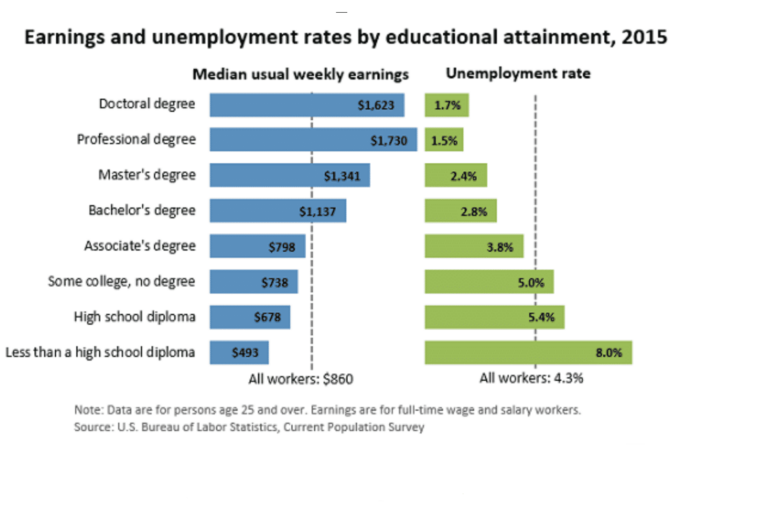
The median salary for a student who has obtained a degree in biology and life sciences range from $36,000 to $110,000 depending on the specific vocational track chosen by each student. Certain concentrations, such as forensic science, pay in the $55,000 range, while biochemists with doctorates can make upwards of $82,000 a year according to the information compiled by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The type of job you pursue in addition to the geographic location you choose will both play a major role in the level of compensation that you can reasonably expect to receive.
Why Choose a Career in Biology?
At the end of the day, your choice is a personal one. Being passionate about biological sciences plus possessing the mental acuity to solve complex problems may set you on the right path. Leverage the best organizations and associations such as the APB to start your research into the biology industry outside academia. For additional resources, make sure to visit MatchCollege and subscribe to our blog for the latest in college information.